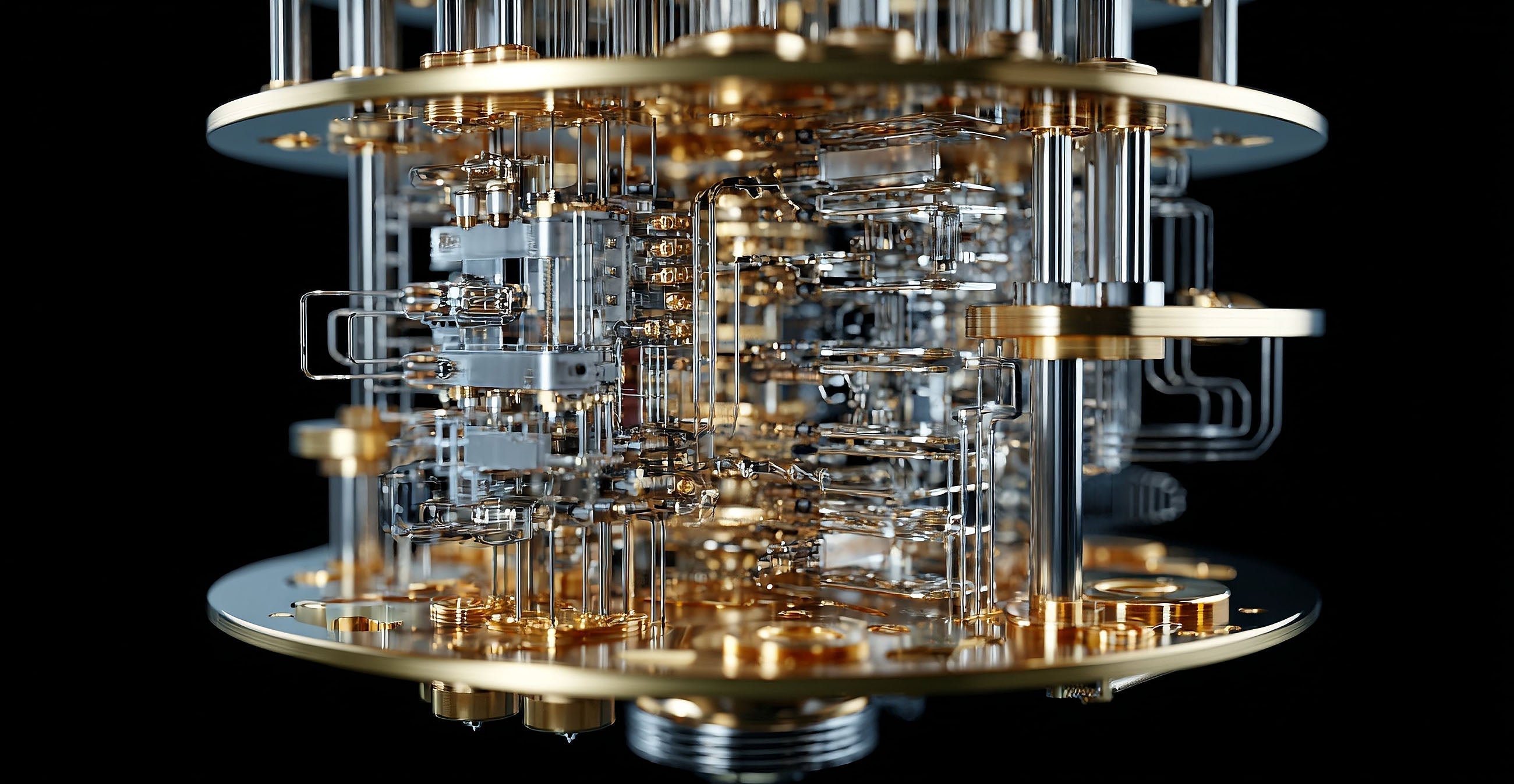
A mechanical watch is a true marvel of engineering and craftsmanship, consisting of hundreds of intricate parts working together to keep time. From the hairspring to the escapement, each component plays a crucial role in the watch's accuracy, functionality, and beauty. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore different parts of a mechanical watch and their functions, as well as the different types of complications and decorative elements that can be found in high-end timepieces. Whether you're a seasoned watch enthusiast or simply curious about how these intricate timepieces work, this guide is sure to deepen your appreciation for the art and science of watchmaking.
1. Balance Spring
The balance spring is a small spring that is attached to the balance wheel. It regulates the oscillation of the balance wheel and helps to keep the watch running accurately.
2. Balance Wheel
The balance wheel is a weighted wheel that oscillates back and forth, providing the timekeeping function of the watch.
3. Escapement
The escapement is the regulating mechanism of the watch. It controls the release of energy from the main spring and regulates the movement of the watch hands.
4. Regulator
The regulator is a mechanism that controls the rate at which the hairspring vibrates, allowing the watch's timekeeping to be adjusted.
5. Pallet Fork
The pallet fork is a small lever that interacts with the escapement wheel and allows the watch to move in small, precise increments.
6. Gear Train
The gear train is a series of gears that transmit power from the main spring to the escapement and balance wheel. It also controls the movement of the watch hands.
7. Crown
The crown is a small knob on the outside of the watch case that is used to wind the main spring and set the time.
8. Dial
The dial is the face of the watch and displays the time and other information such as the date or a chronograph function.
9. Hands
The watch hands are attached to the movement and indicate the time on the dial.
10. Case
The case is the outer shell of the watch that protects the movement from damage and provides a means for attaching the watch to a strap or bracelet.
11. Rotor
The rotor is a weighted mechanism that rotates freely inside the watch case and winds the main spring as it moves.
12. Crystal
The crystal is a transparent cover that protects the dial and hands from dirt and damage.
13. Sapphire Crystal
Sapphire crystal is a type of watch crystal that is highly scratch-resistant and durable. It is commonly used in high-end watches.
14. Strap/Bracelet
The strap or bracelet is the means by which the watch is attached to the wrist. It can be made of leather, metal, or other materials.
15. Bridges
Bridges are metal plates that hold the different parts of the movement in place. They help to keep the parts aligned and provide stability to the movement.
16. Jewels
Jewels are small, synthetic rubies that are used as bearings in the movement. They help to reduce friction between the moving parts and extend the life of the watch.
17. Pinions
Pinions are small gears that are used to transfer power between different parts of the movement.
18. Ratchet Wheel
The ratchet wheel is a gear that is attached to the main spring barrel. It allows the main spring to be wound up by the user or by an automatic winding mechanism.
19. Barrel
The barrel is a cylindrical container that holds the main spring. It also contains gears that transmit power to the rest of the movement.
20. Escape Wheel
The escape wheel is a small gear that moves back and forth, interacting with the pallet fork to regulate the movement of the watch.
21. Pallet Stones
The pallet stones are small pieces of ruby or sapphire that interact with the escape wheel and pallet fork to regulate the movement of the watch.
22. Barrel Arbor
The barrel arbor is a small shaft that connects the main spring barrel to the gear train of the movement.
23. Crown Wheel
The crown wheel is a gear that allows the user to adjust the time and date on the watch.
24. Setting Lever
The setting lever is a small lever that interacts with the crown wheel to allow the user to set the time and date on the watch.
25. Train Wheel
The train wheel is a gear that helps transmit power from the barrel to the rest of the movement.
26. Bezel
The bezel is a ring around the outside of the watch case that can be used for various functions, such as tracking elapsed time or measuring distances.
27. Bi-Directional Bezel
A bi-directional bezel is a type of bezel that can be rotated in both directions. It is typically used in watches that are designed for diving or other activities where elapsed time is important.
28. Chronograph Mechanism
A chronograph mechanism allows the watch to function as a stopwatch, with additional sub-dials or hands to track elapsed time.
29. Chronograph Pushers
The chronograph pushers are buttons on the side of the watch that are used to start, stop, and reset the chronograph function.
30. Chronograph Registers
The chronograph registers are sub-dials on the watch that show the elapsed time for the chronograph function. They may track seconds, minutes, or hours.
31. Chronograph Clutch
The chronograph clutch is a mechanism that engages and disengages the chronograph function from the rest of the movement.
32. Flyback Chronograph
A flyback chronograph is a type of chronograph function that allows the user to reset and restart the chronograph with a single press of a button.
33. Bi-Compax Chronograph
A bi-compax chronograph is a type of chronograph function that features two sub-dials for measuring elapsed time. It typically tracks seconds and minutes.
34. Tourbillon Mechanism
A tourbillon mechanism is a complex system of gears and levers designed to offset the effects of gravity on the movement of the watch. It is a feature found in some high-end mechanical watches.
35. Tourbillon Bridge
The tourbillon bridge is a decorative element found in some tourbillon watches. It is a small, curved bridge that holds the tourbillon cage in place.
36. Tourbillon Cage
The tourbillon cage is a small, rotating cage that holds the balance wheel and escapement. It was invented to counteract the effects of gravity on the movement of the watch, and is found in some high-end watches.
37. Double Tourbillon Mechanism
A double tourbillon mechanism is a type of tourbillon found in some high-end watches. It consists of two separate tourbillon cages, which rotate at different speeds to further improve the watch's accuracy.
38. Gyrotourbillon Mechanism
A gyrotourbillon mechanism is a type of tourbillon found in some high-end watches. It consists of a tourbillon cage that rotates on multiple axes, providing even greater accuracy and regulation.
39. Tri-Axial Tourbillon
A tri-axial tourbillon is a type of tourbillon that features three tourbillon cages rotating on different axes. It provides even greater accuracy and regulation than a double or single tourbillon.
40. Minute Repeater Mechanism
A minute repeater mechanism is a complex system of gears and levers that allows the wearer to hear the time in an audible format.
41. Repeater Snails
The repeater snails are small, toothed wheels that are used in minute repeater watches to determine the current time and chime the appropriate number of times.
42. Minute Repeater Hammers
The minute repeater hammers are small levers that strike the repeating gongs to chime the time in a minute repeater watch.
43. Minute Repeater Gongs
The minute repeater gongs are small metal rods that are struck by the minute repeater hammers to chime the time.
44. Minute Repeater Slide
The minute repeater slide is a small lever or button on the side of the watch that activates the minute repeater function. When pressed, it causes the repeating gongs to chime the time.
45. Minute Repeater Slide Spring
The minute repeater slide spring is a small spring that helps to hold the minute repeater slide in place. It ensures that the slide stays in the correct position and is easy to activate.
46. Minute Repeater Snail
The minute repeater snail is a small, spiral-shaped cam that helps to regulate the chimes produced by the minute repeater function.
47. Minute Repeater Governor
The minute repeater governor is a small, spinning component that helps regulate the speed of the repeating gongs in a minute repeater watch.
48. Moon Phase Indicator
A moon phase indicator is a feature found on some watches that displays the current phase of the moon.
49. Moon Phase Wheel
The moon phase wheel is a small gear that rotates once every 29.5 days, displaying the current phase of the moon on the watch.
50. Moon Phase Sub-Dial
A moon phase sub-dial is a small sub-dial on the watch that displays the current phase of the moon.
51. Perpetual Calendar Mechanism
A perpetual calendar mechanism is a complicated system of gears and levers that automatically adjust the date on the watch, accounting for leap years and months of different lengths.
52. Perpetual Calendar Moon Phase
A perpetual calendar moon phase is a feature found on some watches that combines a perpetual calendar mechanism with a moon phase indicator.
53. Perpetual Calendar Sub-Dial
A perpetual calendar sub-dial is a small sub-dial on the watch that displays the date, day, and month. It is typically found on watches with perpetual calendar mechanisms.
54. Power Reserve Indicator
A power reserve indicator is a feature found on some watches that displays the amount of power remaining in the main spring. It can be in the form of a hand, sub-dial, or other indicator.
55. Flywheel
A flywheel is a rotating mass that is used in some watch movements to maintain a constant level of energy output. It helps to regulate the movement of the watch and maintain accuracy.
56. Shock Absorber
A shock absorber is a mechanism that helps protect the movement from damage due to sudden impacts or jolts.
57. Geneva Stripes
Geneva stripes are a decorative pattern that is often applied to the movement plates of high-end watches. They add a touch of elegance and sophistication to the watch.
58. Perlage
Perlage is another decorative pattern that is often applied to the movement plates of high-end watches. It consists of a series of small, circular patterns that add visual interest to the watch.
59. Engraving
Engraving is a technique used to add decorative designs or text to the watch case or movement. It can be done by hand or with the use of a laser.
60. Jeweled Bearings
In addition to synthetic rubies, some high-end watches use other types of precious stones such as diamonds or sapphires as jeweled bearings. These stones help to reduce friction and wear on the movement, and also add a touch of luxury to the watch.
61. Push-Button Deployant Clasp
The push-button deployant clasp is a type of watch clasp that is easy to use and secure. It typically consists of a small button that releases the clasp when pressed.
62. Co-Axial Escapement
The co-axial escapement is a type of escapement that was invented by watchmaker George Daniels. It reduces friction and wear on the movement, resulting in improved accuracy and longer service intervals.
63. Silicon Components
Some modern watches use silicon components in the movement, such as balance springs or escapement wheels. Silicon is a lightweight and durable material that is resistant to temperature changes and magnetic fields, making it ideal for use in a watch movement.
64. Silicium Escapement
The silicium escapement is a type of escapement that uses silicon components instead of traditional metal components. It is highly resistant to wear and requires less maintenance than traditional escapements.
65. GMT Function
A GMT function is a feature found on some watches that allows the wearer to track a second time zone. It typically consists of an additional hand or sub-dial on the watch.
66. GMT Hand
A GMT hand is an additional hand on the watch that is used to track a second time zone. It typically rotates once every 24 hours and can be adjusted independently of the main timekeeping function.
67. Dual Time Zone
A dual time zone is a feature found on some watches that allows the wearer to track two different time zones simultaneously. It typically consists of an additional hand or sub-dial on the watch.
68. Multiple Time Zone Display
A multiple time zone display is a feature found on some watches that allows the wearer to track the time in multiple time zones simultaneously. It typically consists of multiple sub-dials or windows on the watch.
69. World Time Function
A world time function is a feature found on some watches that allows the wearer to track the time in multiple time zones simultaneously. It typically consists of a rotating bezel or secondary dial on the watch.
70. Chronometer Certification
Chronometer certification is a certification that is awarded to watches that meet strict accuracy standards set by the Swiss Official Chronometer Testing Institute (COSC).
71. Perlage
Perlage is a decorative pattern that is often applied to the movement plates of high-end watches. It consists of a series of small, circular patterns that add visual interest to the watch.
72. Geneva Seal
The Geneva Seal, also known as the Poinçon de Genève, is a certification that is awarded to high-end watches that meet strict quality and finishing standards. Watches that bear the Geneva Seal must be made in the Canton of Geneva and meet a number of specific criteria.
73. Guilloché Dial
A guilloché dial is a type of dial that features a pattern of engraved lines. The pattern is typically very intricate and adds a level of sophistication to the watch.
74. Barrel Arbor Hook
The barrel arbor hook is a small hook that engages with the teeth of the main spring barrel to transmit power to the movement.
75. Barrel Arbor Ratchet
The barrel arbor ratchet is a small gear that is attached to the main spring barrel. It engages with the click wheel to prevent the main spring from unwinding too quickly.
76. Twin Barrel
A twin barrel is a feature found in some watches that uses two main springs to provide extra power and improve accuracy.
77. Click Wheel
The click wheel is a small, toothed wheel that engages with the barrel arbor ratchet to control the release of energy from the main spring.
78. Regulating Pin
The regulating pin is a small pin that is used to adjust the rate of the watch. By moving the pin slightly, the watchmaker can adjust the position of the hairspring and fine-tune the movement.
79. Winding Pinion
The winding pinion is a small gear that is attached to the crown. When the crown is turned, the winding pinion engages with the barrel arbor to wind the main spring.
80. Date Disc
The date disc is a small disc that displays the date on the watch. It is typically located beneath the dial and is adjusted by the user via the crown.
81. Lugs
The lugs are the small protrusions on the side of the watch case that allow the watch to be attached to a strap or bracelet.
82. Exhibition Caseback
An exhibition caseback is a transparent cover on the back of the watch case that allows the wearer to see the movement in action.
83. Telemeter Scale
A telemeter scale is a scale on the watch that is used to measure distance. It is typically located around the outside edge of the dial and is used in conjunction with the chronograph function.
84. Tachymeter Scale
The tachymeter scale is a scale on the watch that is used to measure speed. It is typically located around the outside edge of the dial and is used in conjunction with the chronograph function.
85. Pulsometer Scale
The pulsometer scale is a scale on the watch that is used to measure the heart rate. It is typically located around the outside edge of the dial and is used in conjunction with the chronograph function.
86. Rattrapante Mechanism
A rattrapante mechanism is a type of chronograph function that allows the wearer to time multiple events simultaneously. It typically consists of two chronograph hands that can be stopped independently.
87. Retrograde Indicator
A retrograde indicator is a feature found on some watches that displays information in a non-traditional way. For example, a retrograde date indicator may use a hand that moves backwards across a semicircular scale to display the date.
88. Fusee
A fusee is a conical-shaped device that helps regulate the release of energy from the main spring. It is typically found in older or antique watches.
89. Côtes de Genève
Côtes de Genève is a type of decorative finishing that is often applied to the movement plates of high-end watches. It consists of a series of parallel lines that add a touch of elegance to the watch.
90. Thermocompensation
Thermocompensation is a feature found in some high-end watches that compensates for changes in temperature to maintain the watch's accuracy.
91. Shock-Proofing
Shock-proofing is a feature found in many watches that helps protect the movement from damage due to sudden impacts or jolts.
92. Perlage
Perlage is a decorative pattern that is often applied to the movement plates of high-end watches. It consists of a series of small, circular patterns that add visual interest to the watch.
93. Hacking Seconds
Hacking seconds is a feature found in some watches that allows the seconds hand to stop when the crown is pulled out, allowing for more precise time setting.
94. Quickset Date
A quickset date is a feature found on some watches that allows the user to quickly adjust the date without having to turn the crown multiple times.
95. Helium Release Valve
A helium release valve is a feature found in some dive watches that releases helium gas that can build up inside the watch during deep dives.
96. Anti-Reflective Coating
An anti-reflective coating is a coating applied to the watch crystal that reduces glare and improves visibility.
97. Super-LumiNova
Super-LumiNova is a type of luminescent material that is used on the hands and hour markers of some watches. It glows in the dark and makes the watch easy to read in low-light conditions.
98. Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen used in the production of watch dials and hands. It emits a steady source of light without requiring any external energy, providing a bright and reliable glow that lasts for years. This makes tritium a valuable component in mechanical watches, enhancing both their functionality and aesthetics.
99. Constant Force Mechanism
A constant force mechanism is a feature found in some high-end watches that helps maintain a constant level of energy output from the main spring, resulting in improved accuracy.
100. Annual Calendar Mechanism
An annual calendar mechanism is a feature found in some watches that automatically adjusts the date for months of different lengths, but requires manual adjustment once a year.
101. Retrograde Day Indicator
A retrograde day indicator is a feature found on some watches that displays the day of the week in a non-traditional way. For example, a retrograde day indicator may use a hand that moves backwards across a semicircular scale to display the day.
102. Exhibition Caseback Display
An exhibition caseback display is a transparent cover on the back of the watch case that allows the wearer to see the movement in action. It may be decorated or engraved to add visual interest to the watch.
103. MegaSonic Quartz Movement
A MegaSonic quartz movement is a type of quartz movement that uses a high-frequency quartz crystal to achieve greater accuracy than standard quartz movements.
104. Sunburst Dial
A sunburst dial is a dial that has a textured, radial pattern that radiates from the center of the dial. It adds visual interest and depth to the watch.
105. Skeletonized Movement
A skeletonized movement is a movement that has been cut away to reveal the internal workings of the watch. It allows the wearer to see the intricate mechanisms in action.
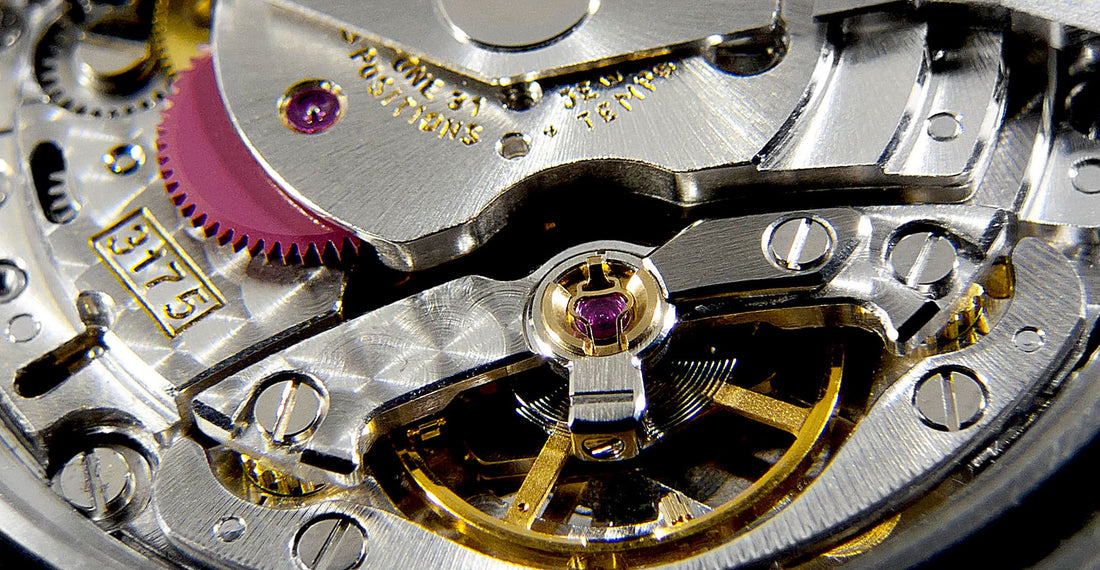

The Comprehensive Guide to Mechanical Watches
13 min read
K. Glissando